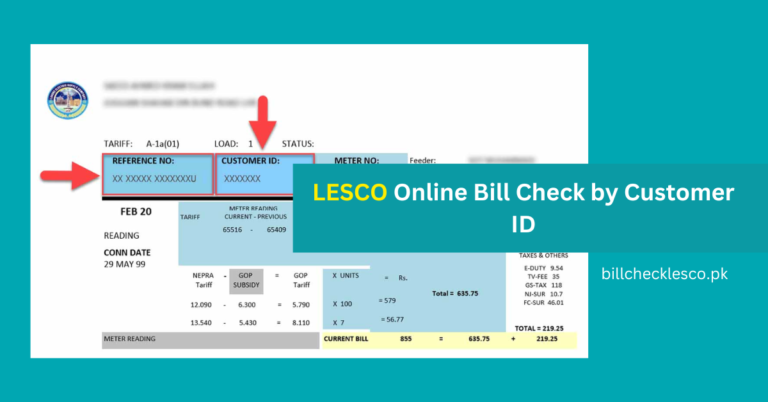
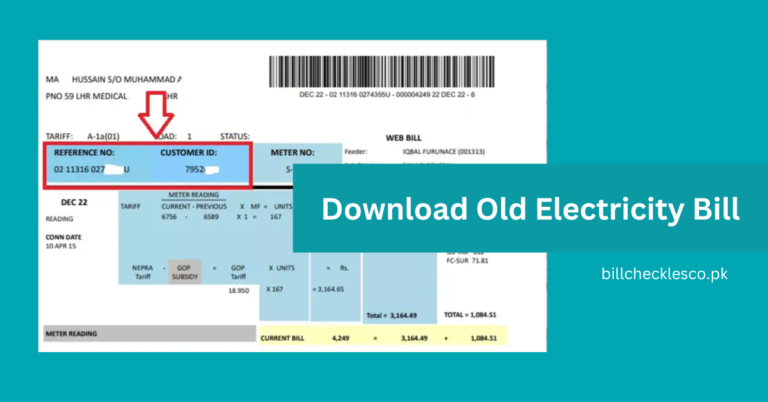
Electricity Meter Reading Units
Electricity meter readings are essential for both households and businesses as they determine the amount of electricity consumed and, consequently, the cost of that consumption. In this article, we will explore various facets of electricity meter reading units, including online readings, calculators, and differences in units across regions such as Pakistan, India, and the UK, digital meters, and the significance of kWh units. Additionally, we’ll inform you how to check electricity meter reading unit rates and prices.
The Basics of Electricity Meter Reading Units
Electricity meters track the consumption of electric power, and the readings from these meters are what utilities use to bill customers. The most common unit of measurement is the kilowatt-hour (kWh). One kWh represents the amount of energy used by a device that draws one kilowatt of power for one hour.
Digital vs. Analog Meters
With the advent of technology, digital electricity meters have become prevalent, replacing the older analog models. Digital meters display readings on an LCD screen, making them easier to read and more accurate than their analog counterparts. These electric meters can also support more sophisticated measurements and services, like time-of-day billing, which can influence how consumers use electricity.
Digital Meters
Operation: Digital meters use electronic components to measure electricity consumption. They are often equipped with more advanced technology than analog meters, including the ability to communicate data back to the utility provider in the case of smart meters.
Display: These meters display consumption data on an LCD or LED screen, showing readings in kilowatt-hours (kWh). Some digital meters cycle through various screens that provide different types of information, such as instant power usage, total consumption, and time-of-use rates.
Accuracy: Digital meters are generally more accurate than analog meters as they can measure energy consumption more precisely and are less susceptible to errors from mechanical wear and tear.
Additional Features: Many digital meters, especially smart meters, offer features like detailed usage reports, remote reading by the utility provider, and the ability to monitor usage in real-time or near-real-time. This can lead to more accurate billing and personalized energy consumption strategies.
Analog Meters
Operation: Analog meters, also known as electromechanical meters, measure electricity using a series of gears and a rotating disc. The speed at which the disc spins correlates to the amount of electricity being used.
Display: The consumption is displayed through a set of dials or a cyclometer that shows the total number of kilowatt-hours consumed. Reading these meters accurately requires interpreting the positions of the dials or numbers, which can be confusing.
Accuracy: While analog meters are quite reliable, their accuracy can degrade over time due to mechanical wear and tear. Additionally, they can be prone to errors from environmental factors or improper readings.
Additional Features: Analog meters are typically more straightforward without the advanced features found in digital meters. They require a manual reading by the homeowner or a utility worker, which can lead to less frequent and potentially less accurate billing based on estimated usage.
Electricity Meter Reading Units Online and Calculators
Many utilities now offer services to check your electricity meter reading units online, providing a convenient way to monitor your energy usage without physically checking the meter.
Additionally, numerous websites and apps feature electricity meter reading unit calculators. These tools can help you estimate your consumption and costs by inputting your previous and current meter readings along with the unit rate.
Electricity Meter Reading Explained
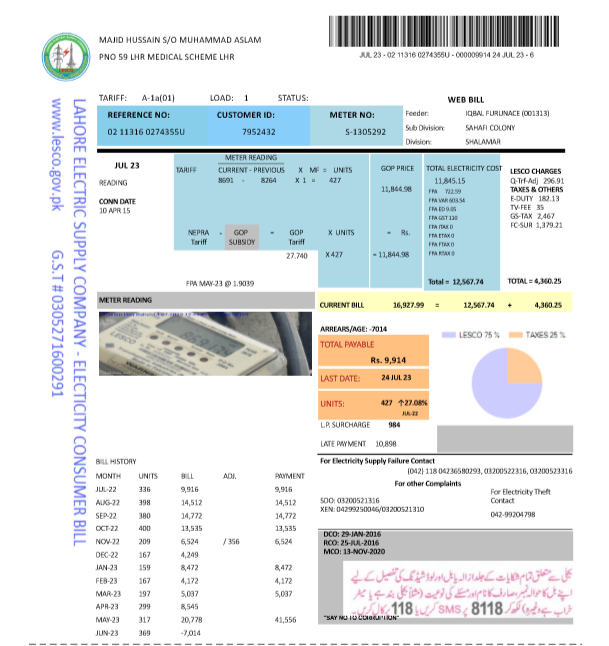
To read your electricity meter, you simply note the kWh displayed. For analog meters, you’ll read the dials from left to right, ignoring any dials marked “1/10” as these record small amounts not used in billing. For digital meters, the display will cycle through various readings; the kWh usage is typically the primary figure.
Lahore Electricity Unit Pricing
The cost per unit of electricity consumed varies with the total units used, as outlined below:
- For consumption up to 100 units, the charge is 5.79 rupees per unit.
- Usage between 101 and 200 units is priced at 8.11 rupees per unit.
- When consumption is between 201 and 300 units, the rate increases to 10.20 rupees per unit.
- For a meter reading of 301 to 700 units, the cost per unit is 17.60 rupees.
- Consumption exceeding 700 units will be charged at a rate of 20.70 rupees per unit.
How to Calculate Electricity Bill in Pakistan? (Manually)
To manually compute your electricity bill, begin by determining the energy usage of each household appliance. For instance, if you operate an electric motor with a 3,000-watt power rating for 5 hours daily, the calculation for daily consumption is as follows:
To ascertain the monthly consumption, multiply the daily consumption figure by 30:
15,000Wh x 30 days = 450,000Wh, or 450 kWh (converting watt-hours to kilowatt-hours by dividing by 1,000).
Applying the Tariff Rate
As of March, Pakistan’s electricity tariff stands at 9.406 PKR per kWh (equivalent to $0.060). To find out your monthly electricity bill, multiply your total monthly consumption in kWh by the tariff rate:
450 kWh x 9.406 PKR per kWh = 4,232.7 PKR
Calculating the bill for every single appliance individually can be a tedious process. For a more straightforward calculation, consider using an online bill calculator.
How to Check Units In Digital Electric Mete?
Checking the units consumed on a digital electric meter is a straightforward process that varies slightly depending on the manufacturer and model of the meter. Generally, digital meters display the electricity usage directly on an LCD screen. To check the units consumed, you would typically look for the display labeled with ‘kWh’, which stands for kilowatt-hours, the standard unit of measurement for electricity consumption. In most cases, the meter cycles through different screens or displays, so you may need to wait a moment for the kWh reading to appear.
Some electric meters have a button that you can press to cycle through the different information displays more quickly.
Note – You should note the current reading and compare it with a previous reading to calculate your electricity consumption over a period. If your meter has more complex functionalities, such as displaying peak and off-peak usage, the instruction manual or a quick online search specific to your meter’s model can provide detailed guidance on interpreting each reading.